
One of OCRE's main objectives was to make the uptake of cloud and digital Earth Observation services easier by proposing new business models that can be applied in Europe and potentially adopted within the European Open Science Cloud to ensure that researchers have access to commercial providers.
OCRE's approach was to engage both the demand side (research community) and the supply side (commercial cloud and EO companies) which would make up the digital single market for commercial cloud and EO services for research. To pilot the business models that OCRE experimented with, the project made use of the €8.5 million funding from the European Commission in funding calls towards research projects.
Procurement Mechanisms
OCRE IaaS+ Framework: Procurement for Commercial Cloud in Research | Multiple Direct Awards: Procurement for EO Services in Research |
OCRE ran a pan-European procurement resulting in 474 framework contracts providing 10,000 institutions and universities across Europe with benefits such as seamless procurement procedure, compliance, and volume discounts. The OCRE Cloud Catalogue showcases the commercial cloud providers and 40 countries covered in the OCRE IaaS+ Framework. | For EO, the project found that since most EO procurements were below European procurement thresholds, multiple direct awards were deemed sufficient for most of the EO procurement activities run under the project. This required gathering requirements for the EO services, running a mini-competition with a shortlist two to three EO suppliers and finally the selection. To enable research projects to easily find EO suppliers OCRE developed the OCRE EO Catalogue. |
Learn more about the OCRE IaaS+ Framework
|
|
Funding Mechanisms
The project had €8.5 million in cloud and EO adoption funding from the European Commission to distribute. Majority of these funds were earmarked to be distributed via the funding mechanisms that will be piloted by the OCRE project. To ensure independent oversight, the project invited external experts into the OCRE External Advisory Board to ensure the fair distribution of cloud and EO funding to research institutions.
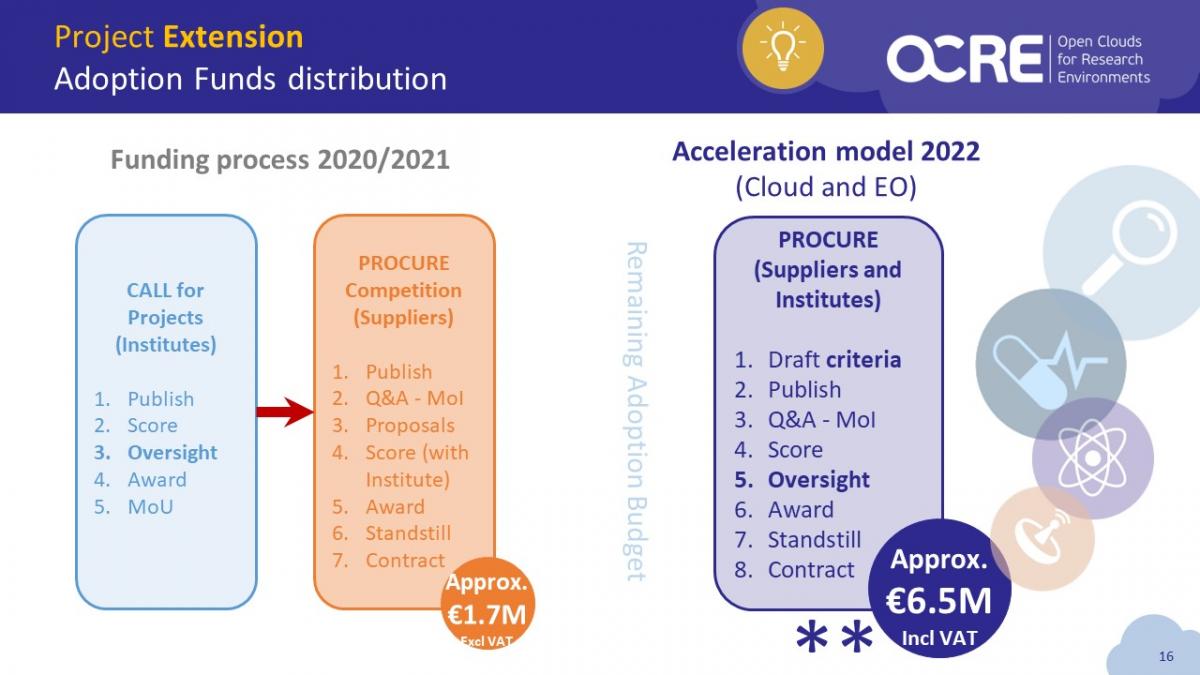 The project ran two funding calls:
The project ran two funding calls:
- 1st OCRE Cloud and EO Funding Calls (2020-2021): Two separate funding calls were run by OCRE, one for EO and one for cloud. The calls were done in two parts: first a call for research projects. This required publishing and promoting the call, scoring the received proposals, oversight of the scoring by the OCRE External Advisory Board, awarding of the funds and signing a memorandum of understanding. The second part was towards the suppliers which required publishing the procurement towards the eligible suppliers as listed in the OCRE Cloud Catalogue, transparently managing supplier inquiries, receiving proposals, scoring the proposals in conjunction with the projects, awarding and finally contracting the awarded supplier, before then proceeding to the consumption of the services.
- 2nd OCRE Cloud and EO Funding Calls (2022 - Accelerated Model): For cloud, this innovative procedure required suppliers and projects to team up and make the submission together (through an OCRE IaaS+ Framework supplier). This required publishing the call, addressing questions, scoring, oversight from the OCRE External Advisory Board, and contracting before proceeding to the consumption of the services. This model eliminates the dual procedure in the first call, and encourages closer collaboration between suppliers and research institutes. For EO, the process was roughly similar to the 1st OCRE EO Funding Call, the only difference was that the OCRE EO Catalogue was launched to support the procurement team and research institutes in the selection of suppliers.
In the first part of the project, OCRE also distributed IaaS vouchers to individual researchers through EuroDoc and the EOSC-hub Early Adopters Programme. Proposal gathering and evaluation was carried out through these voucher distributors. One supplier from the previous GÉANT IaaS framework (the predecessor of the OCRE IaaS+ Framework) was selected. The allotted budget and the use of the then already existing IaaS Framework even allowed for immediate allocation towards an emergency situation such as the COVID pandemic.
Impact and Success Stories
Overall, the funding calls allowed the project to test out the procurement and funding procedures and to come up with an accelerated model. It also resulted in use cases that will further encourage the uptake of commercial cloud and EO in research by demonstrating their value to European research. Check out diverse use cases from our funding calls:
Policy Brief
Throughout the project, OCRE engaged with numerous researchers across Europe and supported them in the procurement process. Although OCRE had an overall understanding of the difficulties faced by researchers in accessing commercial cloud services, it was also fundamental to inquire about specific challenges and needs across fields and find common issues and potential solutions. Following a set of online interviews complemented by questionnaires, the OCRE team has collected the major obstacles faced by the research community and recommendations on how to improve access to cloud resources in a policy brief.
Read the OCRE Policy Brief now!
Overall, the funding calls allowed the project to test out the procurement and funding procedures and to come up with an accelerated model. It also resulted in use cases that will further encourage the uptake of commercial cloud and EO in research by demonstrating their value to European research. Check out diverse use cases from our funding calls:
The OCRE IaaS Framework has also provided the European research community and the European Open Science Cloud, particularly the EOSC Exchange (see EOSC Symposium 2022, EOSC Exchange Capabilities session - EOSC Future) with a significant number of commercial providers, easier procurement pathways, funding distribution models and a potentially stronger bargaining power towards commercial providers by ensuring the best offerings are made available to research institutes.
